Candidiasis can be described as a fungal infection that is caused by Candida yeast, a type of fungus. Candida albicans is the most common Candida species that can cause infection. Candida is found on the skin and in the body. It can be found in the mouth, throat and gut. Candida can cause infection if it grows beyond control or enters the body’s internal organs, such as the bloodstream, kidneys, heart, and brain.
Candidiasis of the throat and mouth is also known as thrush. Candidiasis in your esophagus, the tube connecting the throat and the stomach, is known as Candida Esophagitis. One of the most common infections among HIV/AIDS patients is esophageal candidiasis.
Symptoms
There are many symptoms of Candidiasis, which can occur in the throat and mouth.
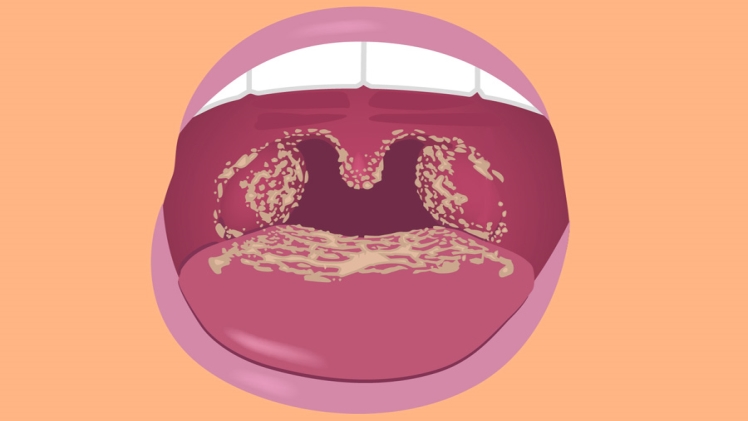
White spots on the cheeks, inner cheeks, roof of mouth, throat, tongue and roof of mouth (photo showing candidiasis).
- Redness and soreness
- Feels like cotton in the mouth
- Loss of taste
- Pain when swallowing or eating
- Cracking and reddening around the corners of your mouth
- Common symptoms of candidiasis include difficulty swallowing and pain in the swallow.
If you experience symptoms you suspect are due to candidiasis, consult your healthcare provider.
Prevention and Risk
Who develops candidiasis of the throat or mouth? Healthy adults are unlikely to experience candidiasis in their mouth, throat or esophagus. Babies, particularly those under 1 month, are more at risk of developing candidiasis in their mouth and throat.
What can I do to prevent candidiasis from my throat or mouth?
There are several ways to prevent candidiasis from the throat and mouth.
- Keep your mouth healthy
- After inhaling corticosteroids, rinse your mouth and brush your teeth.
Sources
Candida is normally found in the throat, mouth, and rest of the digestive system. Candida can sometimes multiply and cause infection if the environment in the mouth, throat, or stomach changes in a way that favors its growth.
It can happen at any time, Especially, if a person’s immune system is weakened. If antibiotics alter the natural balance microbes in your body, Or for many other reasons in different groups of people.
Diagnostics and Testing
A healthcare provider can diagnose candidiasis by simply looking inside the mouth and throat.8 The sample is sent to the laboratory for testing. It will usually be examined under a microscope.
Endoscopy is a procedure that allows healthcare providers to diagnose candidiasis of the esophagus. Endoscopy allows for the examination of the digestive tract with a tube equipped with a light source and a camera. To determine if the patient’s symptoms improve, a healthcare provider may prescribe antifungal medication without performing an endoscopy.
Treatment
Antifungal medicine is used to treat mild to moderate cases of Candidiasis.6 This treatment is typically for the inside of the mouth and lasts 7 to 14 days. Clotrimazole and miconazole are some of the most common antifungal medications. Fluconazole, an antifungal medication that can be taken either by mouth or via a vein, is the best treatment for severe infections. Healthcare providers can prescribe another antifungal if the patient doesn’t respond to fluconazole. Fluconazole is the most common treatment for candidiasis of the esophagus. For those who are unable to take fluconazole, or for those who do not feel better after taking fluconazole, there are other prescription antifungal medications.